Edition 4
Published on 3/11/2024
This Edition Covers the Interconnected World of Blockchain, Smart Contracts and so much more!
Sneak Peak Into Blockchain 👀
A blockchain is a digital ledger which is a technology that records transactions but here in a secure, decentralized, and transparent manner, forming an immutable chain of blocks.
An asset can be tangible (a house, car, cash, land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding). Virtually anything of value can be tracked and traded on a blockchain network, reducing risk and cutting costs for all involved.
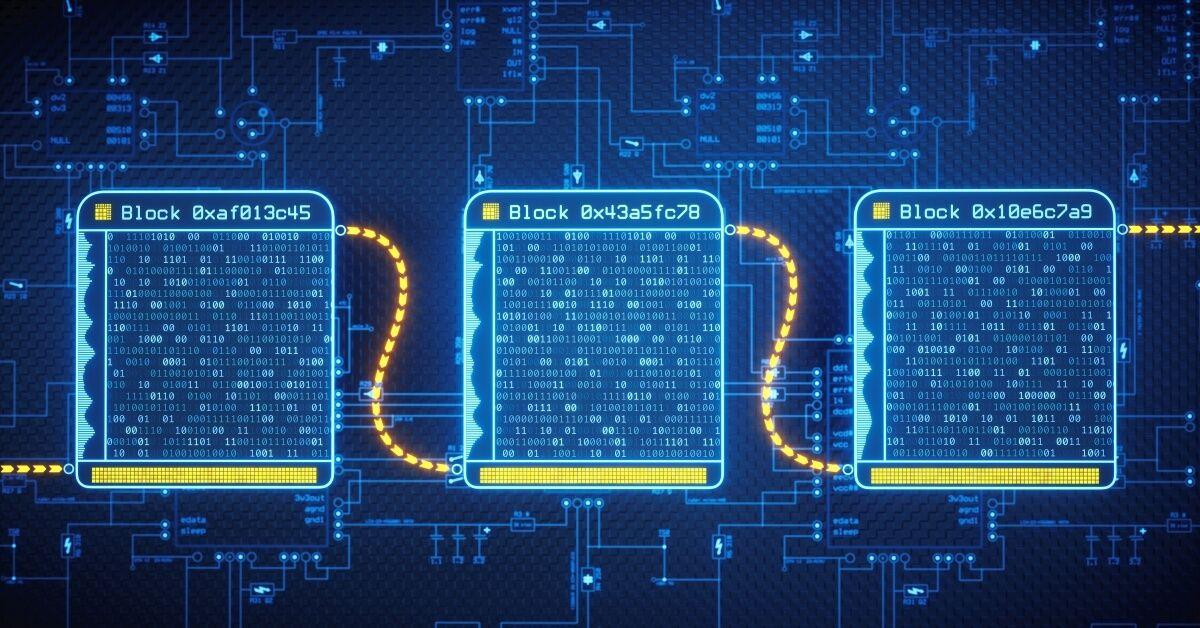
How blockchain works-
- Each transaction is recorded as a "block" of data, showing asset movement and details like who, what, when, where, and quantity.
- Blocks are connected to form an irreversible chain, ensuring the sequence and time of transactions.
- This chain, or blockchain, is tamper-evident and trusted by network members due to its immutability and verification process.

How Exactly is it Tamperproof?
Each block also contains a unique code, called a hash, that's generated based on the data in the block. This hash acts like a digital fingerprint for the block.
Now, here's the cool part: each block also includes the hash, a string of random letters derived from file content, of the previous block. So, if you try to change anything in a block, its content changes thus altering its hash. Since the altered block's hash won't match the hash stored in the next block, it will be immediately apparent that something has been tampered with.
Think of it like a chain of blocks (hence the name "blockchain"), where each block is securely connected to the previous one. If you try to mess with one block, you'll break the chain, and everyone will notice. This makes blockchain tamperproof because any attempt to alter the data in a block would require changing every subsequent block, which is computationally infeasible and easily detectable.
Key elements
- Distributed Ledger Technology: All network participants have access to an immutable record of transactions, reducing duplication of effort.
- Immutable Records: Transactions recorded on the shared ledger cannot be changed or tampered with, ensuring transparency and accuracy.
- Smart Contracts: Automated execution of predefined rules, known as smart contracts, streamlines transactions for various purposes like corporate bond transfers and insurance payments.
- Public key cryptography in blockchain uses two keys: a common public key and a unique private key for each member. They work together to secure data on the ledger.
Importance
Blockchain provides real-time, shared, and transparent information stored securely on an immutable ledger. It efficiently tracks orders, payments, production, and other activities with access restricted to permissioned network members. Its single perspective on reality ensures confidence, efficiency, and new opportunities for businesses.
Use in different Industries
Blockchain is an emerging technology that is being adopted innovatively by various industries:
- Finance: Blockchain services are utilized for online payments, account management, and market trading in traditional financial systems.
- Media and Entertainment: Blockchain systems manage copyright data, ensuring fair compensation for artists.
- Retail: Blockchain is used to track the movement of goods between suppliers and buyers in the retail sector.
Next Big Idea 💡
Smart contracts are self-executing programs that live on blockchains, enabling the automatic fulfilment of agreements between parties. They consist of code containing conditional statements ("if/when...") that trigger actions when predefined conditions are met.
To establish a smart contract, participants negotiate the terms and publish the contract on the blockchain. Once the contract becomes active, it cannot be revoked or altered without consensus from the network. If necessary, an external source known as an "oracle" provides updated information to the blockchain, ensuring that the contract remains relevant to the real world
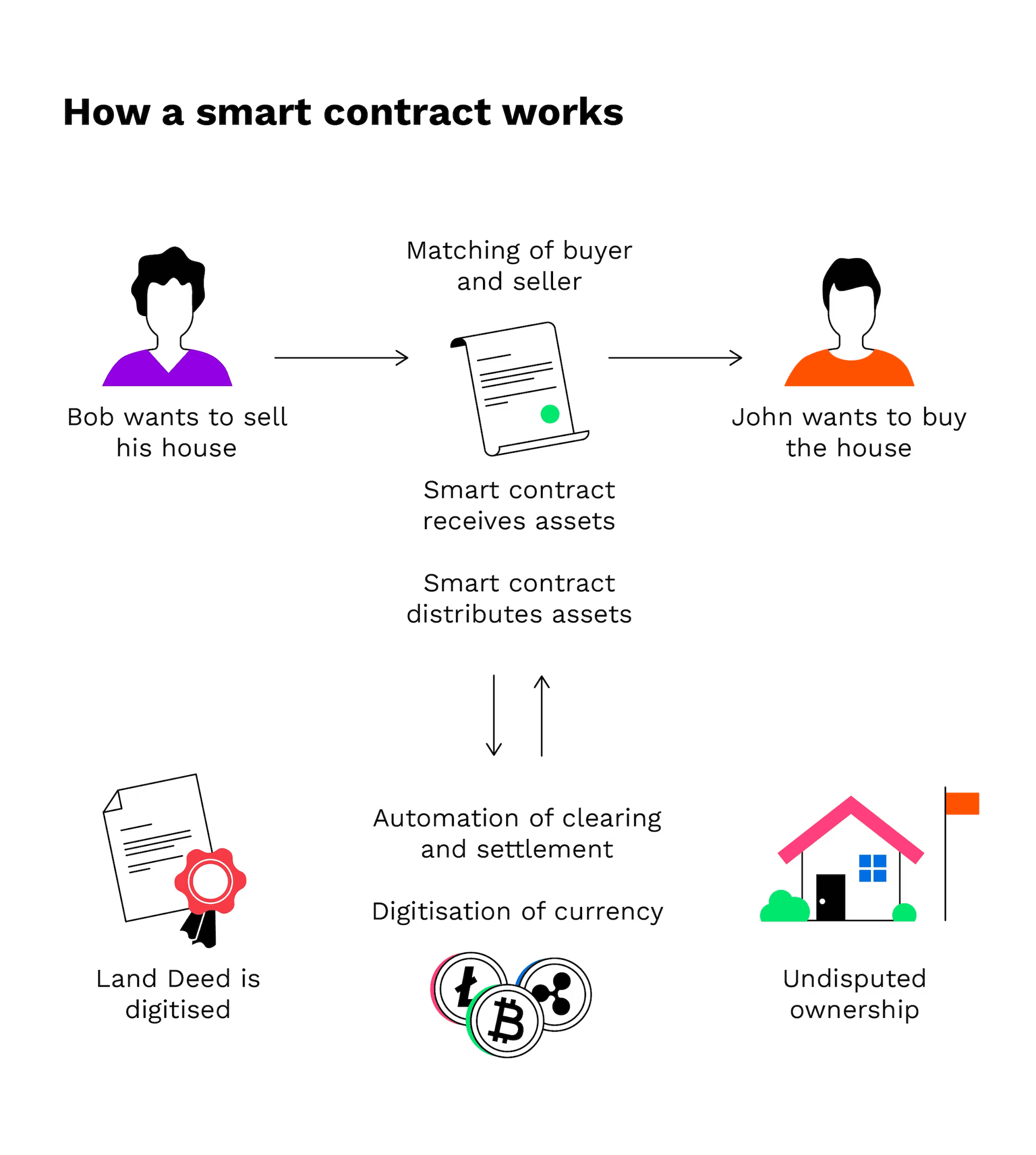
The main components of a smart contract are:
- Agreement: Parties define the terms and conditions of the contract.
- Creation: Developers compile the contract into code and submit it to the blockchain.
- Activation: After validation, the contract becomes active on the blockchain and cannot be reversed or altered.
- Monitoring: Conditions are checked against the blockchain or external sources.
- Execution: Upon meeting the conditions, the smart contract performs the specified actions
Smart contracts facilitate efficient, transparent, and secure transactions across industries, reducing risks and eliminating the need for intermediaries
Legal Issues with Blockchains and Smart Contracts
Blockchains' openness makes protecting private information difficult because once recorded, data cannot easily be changed or hidden. This creates challenges when complying with privacy laws.
Innovative solution
Blockchain technology has revolutionised the way we store and transfer data, but it also poses a significant challenge to data privacy. To address this issue, an innovative solution involves decentralised identity management using advanced cryptography like zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) and homomorphic encryption.
This approach allows users to verify their identity without revealing personal data, ensuring the secure use of blockchain services while maintaining control over their information.
By using ZKPs, users can prove their credentials without disclosing sensitive information, while homomorphic encryption enables computations on encrypted data, ensuring privacy in blockchain transactions. This combination reduces the risk of unauthorised access and ensures compliance with data protection laws.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are a type of technology that uses blockchain to make digital transactions more secure, transparent, and automated. They can improve data quality and solve challenges like skill gaps and insufficient support. To benefit from this technology, organisations need to learn how to develop and use smart contracts.
Recommendations And Reviews 📚
Awesome Blockchain
Awesome Lists on Github are a bunch of repositories containing all the resources in the world about specific topics! This is a curated list of resources for the development and applications of blockchain. Whether you're a novice or an expert developer, this collection covers everything from foundational guides to advanced topics like Ethereum development, big projects such as Bitcoin and Hyperledger, and cutting-edge discussions on scalability, privacy, and consensus mechanisms.
🔗 : https://github.com/yjjnls/awesome-blockchain/tree/master
Blockchain Basics by IBM
IBM's "Blockchain Basics" course is a good starting point for understanding blockchain. It explains important concepts like how blockchain works and its uses. While it might be too simple for some, it's great for beginners who want to learn the basics. IBM is known for its commitment to education and innovation, and this course reflects that.
🔗 : https://developer.ibm.com/learningpaths/get-started-blockchain/